
Canadian Taiga Cordillera Location
The Taiga Cordillera is an ecosystem found largely extending on the border of the Yukon territory. It is an area largely unharmed by glacial action. Many landforms varying in elevation and size can be found here, some of these are:
Talus slopes
Hoodoos
Folded mountain
Braided river channel
Craggy limestone peaks and ridges
Butte
Alluvial fan
Sedimentary rock
Fault
Cave
Stone stripes
Stone polygons
Brachiopod fossils
Coral fossils
- Gastropod fossils
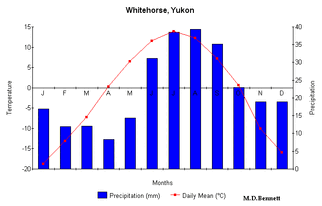
The Taiga Cordillera makes up the northern part of the Rocky Mountains in Canada and contains some of the highest waterfalls, deepest canyons, and most insane rivers.As an example, while it is near the edge of the taiga cordillera, Whitehorse, in the Yukon territory is a city that faces some of the taiga cordillera's extremes.
Mountains block most of the precipitation, while averages 250 to 300mm per year, its northern position gives it extremely cold winters with a -22 Degrees Celsius average temperature, this area also has short days and short cool summers, which average at 8 Degrees Celsius. The snow on the ground lasts for six to eight months a year. Taiga Cordillera has a very diverse and and interesting geological makeup, most of the Cordillera is covered with steep mountains, although the NorthWest contains wetlands and rolling hills, and to the direct north there is the Tundra. The Tundra is above the treeline, so only small plants and shrubs grow here.
The Taiga Cordillera also has many instances of Flora and Fauna. As the area you look in determines what plants you will find, for instance you will find large, leafy abundant plants on the Western side, as it receives and blocks most of the precipitation. And the north side of the mountain range is sparse in terms of vegetation, it consists of only shrubs, as it is past the tree line.Paper birch, alpine fir, lodgepole pine, black spruce, white spruce, balsam poplar, water birch, Alaska paper birch, blue-green willow, Bebb willow, and net-veined willow. Not only is it home to many varieties of tree, but also many shrubs, including sedge, cottongrass, Labrador tea, & fire snag. Just like with plants, the animals you find are entirely based on the area you look in .Large carnivores that are found here include black bear, grizzly bear, wolf and lynx. The large herbivores include Dall’s sheep, caribou,moose, and mountain goat. The Taiga Cordillera is made up of all types of rock, metamorphic, sedimentary, and igneous. This was caused by the volcanic eruptions that formed the area, settling after the eruptions, and then eventually glaciation.
Sourcing: no Authors, Dates/Times, or Publishers given.
http://ecozone-experts.wikispaces.com/Taiga+Shield
http://ecozone-experts.wikispaces.com/Taiga+Cordillera
http://ecozones.ca/english/zone/TaigaCordillera/land.html
http://www.emr.gov.yk.ca/oilandgas/pdf/bmp_taiga_cordillera_ecozone.pdf